What is a PBX phone system?
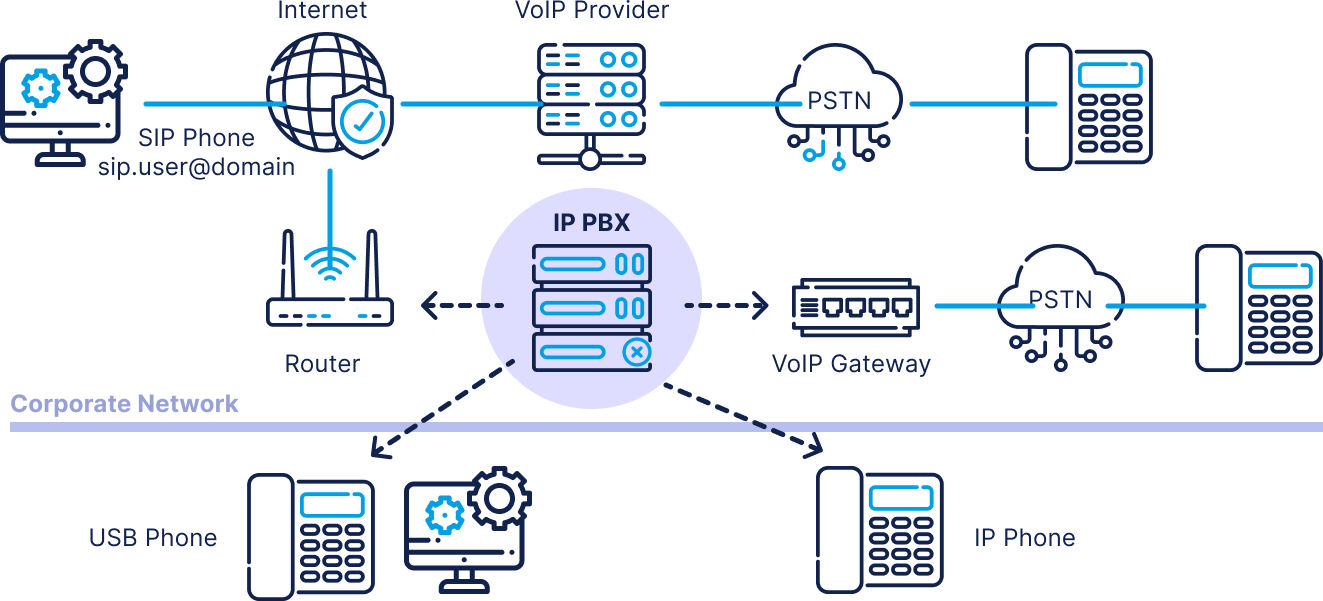
A PBX (Private Branch Exchange) phone system is a private telephone network used within an organization. Users within the company can communicate internally and externally (with the outside world), using different communication channels like Voice over IP (VoIP), ISDN, or analog. A PBX allows organizations to have more phones than physical phone lines and allows free calls between users.
Table of Contents
- What is a PBX phone system?
- How does a PBX work?
- Features of a PBX
- The purpose of a PBX
- PBX System Benefits for Businesses
- Types of PBX phone systems
- What are the benefits of a PBX system?
- What to look for in a PBX system
- Adapt a PBX to Your Company — Not the Other Way Around
- Why choose RingQ as your business phone system?
- PBX Phone System FAQs
How does a PBX work?
A PBX (Private Branch Exchange) works as a centralized system that manages and routes calls within an organization. Here’s how it works step by step:
- Call Handling
- Incoming Calls: When an external call comes in, the PBX system receives it through the organization’s phone lines (traditional lines or via VoIP) and routes the call to the appropriate internal extension based on pre-set rules (e.g., direct dial, operator, or an IVR system).
- Outgoing Calls: When an internal user makes a call, the PBX connects them to an external phone line (PSTN or VoIP service) and handles the routing outside the organization.
- Call Routing and Switching
The PBX switches calls between internal users or between internal and external lines. It functions similarly to a telephone switchboard operator but automatically and more efficiently.
- Internal Communication: Employees can call each other via short extension numbers without going through external lines. For example, one department can call another without dialing a full phone number.
- External Communication: The PBX allocates the available phone lines (or VoIP connections) for outbound or inbound external calls.
- Connecting to the PSTN or VoIP Networks
The PBX is connected to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) for traditional landlines or to the internet in the case of VoIP (IP PBX systems). This connection allows the PBX to manage both internal calls and external calls coming in from or going out to the outside world.
- Extensions and Features
- PBX allows businesses to have multiple phone extensions (i.e., internal phone numbers) without needing a separate external line for each phone.
- Call transfers, conference calls, call forwarding, and other features are part of the PBX’s functionality.
- Cost Efficiency
By centralizing and managing the organization’s telecommunication needs, PBX systems reduce the need for multiple phone lines and minimize call costs, especially for internal communication.
In summary, PBX serves as an efficient call management system within an organization, routing calls internally between users and externally through outside networks like PSTN or VoIP.
Features of a PBX
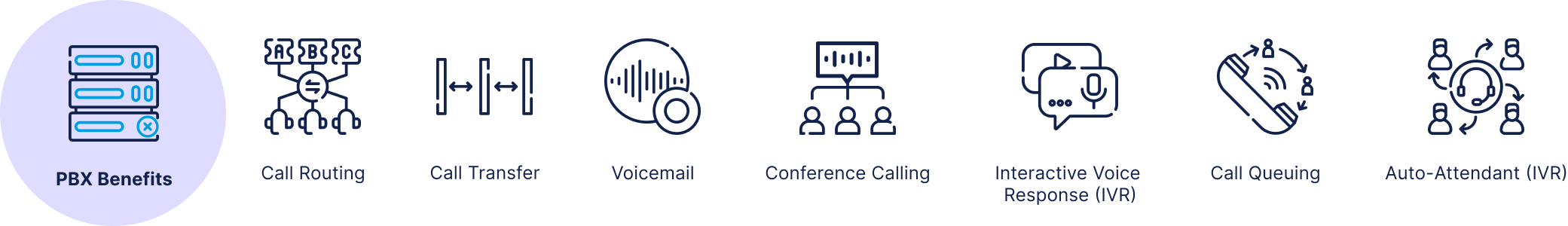
Key features of a PBX system include:
- Call Routing: Automatically directs incoming calls to the appropriate extensions.
- Call Transfer: Allows users to transfer calls to another internal or external number.
- Voicemail: Provides voicemail services for users who can’t answer calls.
- Conference Calling: Supports multi-party calls.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR): An automated system that interacts with callers through voice prompts and touch-tone input.
- Call Queuing: Places incoming calls in line if no one is available to take them.
- Auto-Attendant (IVR): A virtual receptionist answers calls and guides callers through options (e.g., “Press 1 for Sales, Press 2 for Support”).
The purpose of a PBX
The primary purpose of a PBX (Private Branch Exchange) is to manage and streamline the communication system within an organization. Here’s a breakdown of its key purposes:
- Internal Call Management
- Efficient Routing of Internal Calls: PBX allows employees to communicate with each other internally through extensions without using external phone lines. This saves money and provides fast, easy communication within the company.
- Extension Dialing: Instead of dialing full phone numbers, employees can reach each other by dialing short extension numbers.
- Handling External Calls
- Incoming Call Routing: PBX directs incoming calls from outside the organization to the appropriate person, department, or extension.
- Outgoing Call Management: PBX manages outbound calls from employees to external numbers, using available phone lines or internet-based (VoIP) connections.
- Cost Efficiency
- Reduced Costs for Internal Calls: Internal calls don’t require external lines, reducing telephone costs.
- Shared Phone Lines: With a PBX, multiple employees can share a smaller number of external phone lines, which minimizes the need for many direct lines and reduces monthly line costs.
- Centralized Control and Management
- Automated Call Handling: PBX automates call routing and management through features like auto-attendant, call forwarding, and voicemail, reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Unified Communication System: It brings together various communication channels (phone calls, voicemail, chat, video, email, fax) into a single system for easier management.
- Scalability and Flexibility
- Easy Expansion: As a business grows, more extensions can be added without the need for new physical phone lines for each user.
- Flexible Call Routing: PBX systems allow for advanced call routing based on criteria like time of day, caller ID, and employee availability, ensuring efficient communication flow.
- Professional Call Management
- IVR/Auto-Attendant: PBX can provide a professional greeting and menu system (Interactive Voice Response), guiding callers to the right department or person.
- Call Queuing: It can handle high call volumes by placing callers on hold and directing them to available agents, enhancing customer experience.
- Advanced Communication Features
- Voicemail, Call Forwarding, and Conferencing: PBX offers advanced features like voicemail, call forwarding, and conference calls, enhancing communication efficiency within the organization.
- Call Recording and Monitoring: For quality control or training purposes, PBX systems may include the ability to record and monitor calls.
In summary, the purpose of a PBX is to centralize, organize, and simplify a company’s internal and external communications, improve cost efficiency, and provide advanced features for managing calls professionally.
PBX System Benefits for Businesses
A PBX system offers numerous benefits to businesses, particularly in managing communication and improving operational efficiency. Here are the key advantages:
- Cost Savings
- Reduced Internal Call Costs: Internal communication between employees using PBX extensions does not require external phone lines, significantly reducing costs.
- Shared External Lines: PBX systems allow multiple employees to share a smaller number of external lines, cutting down on the need for individual lines for each user.
- VoIP Integration: IP PBX systems can leverage the internet for calls (VoIP), which can be cheaper than traditional phone lines, especially for long-distance and international calls.
- Improved Call Management and Routing
- Automated Call Routing: PBX systems automatically route calls to the correct department or employee, reducing manual intervention and improving efficiency.
- Professional Call Handling: Features like auto-attendant (IVR) and voicemail ensure calls are handled professionally even when staff are unavailable.
- Call Queuing: High-volume businesses can place incoming calls in queues, ensuring callers are handled in an orderly and efficient manner.
- Enhanced Communication Features
- Voicemail and Voicemail-to-Email: Employees can access voicemails from anywhere, improving response times. Some PBX systems even send voicemail messages to email for easier management.
- Call Forwarding and Mobility: Calls can be forwarded to mobile phones or remote extensions, allowing employees to stay connected even when they’re out of the office.
- Audio & Video Conference Calling: Built-in conference features make it easier for teams to collaborate without needing separate conferencing solutions.
- Scalability
- Easy Expansion: PBX systems are highly scalable. As the business grows, adding new extensions or phone lines is straightforward without significant hardware changes or additional costs.
- Flexible Deployment: Whether it’s a small startup or a large corporation, PBX systems can be tailored to meet specific needs and grow alongside the business.
- Centralized Control and Management
- Single Point of Control: A PBX system centralizes the management of the company’s communications, allowing IT departments to oversee all phone lines and users from one location.
- Advanced Reporting: Many PBX systems provide call logs and detailed reports, helping businesses monitor call volumes, durations, and patterns for better resource management.
- Call Recording: PBX systems often support call recording, which can be used for training, quality assurance, or legal purposes.
- Better Customer Service
- Auto-Attendant: An auto-attendant feature ensures that incoming calls are greeted and routed efficiently, improving the caller’s experience.
- Call Routing Rules: Calls can be routed based on time of day, employee availability, or caller identity, ensuring that important calls are handled promptly.
- Call Queuing: PBX systems manage high call volumes effectively, keeping customers informed about their wait times and ensuring calls are answered when someone becomes available.
- Mobility and Remote Work Support
- Remote Extensions: PBX systems can connect remote workers, allowing them to access the company’s phone system as though they were in the office.
- Mobile Integration: Calls can be forwarded to mobile devices, ensuring employees remain accessible while on the go or working remotely.
- Increased Reliability and Uptime
- Redundancy and Failover: PBX systems, especially hosted/cloud PBX, offer redundancy features to keep phone lines up and running, even during local outages or technical failures.
- Cloud-Based Options: Hosted PBX systems are maintained by third-party providers with high reliability and uptime guarantees, eliminating the need for businesses to worry about maintaining physical hardware.
- Security
- Controlled Access: PBX systems allow businesses to secure their communications with features like encryption, user authentication, and call logging.
- Monitoring and Auditing: PBX systems often include call monitoring and auditing features that can help detect and prevent fraud or misuse.
- Integration with Business Tools
- CRM Integration: Many modern PBX systems integrate with Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, automatically linking calls to customer records and improving tracking.
- Unified Communications: PBX systems can unify voice, video, email, and chat, creating a seamless communication platform for employees.
In summary, PBX systems provide businesses with a centralized, cost-effective, and scalable communication solution. They offer advanced features that improve call handling, customer service, and operational flexibility, making them an essential tool for businesses looking to streamline communications.
Types of PBX phone systems

On-Premise PBX
(Traditional PBX)
An on-premise PBX system is physically located at the business’s premises, and the organization is responsible for maintaining and managing the system. It typically connects to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) via traditional phone lines or through SIP trunking for VoIP-based communication.
Key Features:
- Physical Hardware: The PBX server and all related equipment (such as phone lines and cabling) are installed and managed on-site.
- In-House Control: Businesses have full control over the system’s configuration and maintenance.
- Customizable: On-premise systems can be highly customizable to meet specific business needs.
Advantages:
- Greater Control: Since the hardware is on-site, businesses have complete control over the configuration, security, and management.
- Custom Configuration: Allows for deep customization, making it ideal for businesses with specific, complex telecommunication needs.
- Long-Term Cost: Once installed, long-term costs can be lower for businesses that prefer not to rely on third-party subscriptions.
Disadvantages:
- High Upfront Cost: Requires a significant upfront investment in hardware, installation, and ongoing maintenance.
- Maintenance and IT Resources: Requires an in-house IT team to manage and maintain the hardware and software.
- Limited Flexibility: Expanding or upgrading the system requires additional hardware, making it less scalable compared to cloud-based options.
Best For:
- Larger organizations or businesses that need complete control over their phone system.
- Companies with dedicated IT staff to manage and maintain the system.

Cloud or
Hosted PBX
A cloud PBX (also known as hosted PBX) is managed and maintained by a third-party provider, with the system hosted on the provider’s servers in the cloud. Businesses access the PBX system via the internet, and there’s no need for on-site hardware (other than the phones).
Key Features:
- No On-Site Hardware: The service provider handles all the infrastructure in the cloud, and businesses access the system through IP phones or softphones over the internet.
- Minimal Maintenance: The provider handles all maintenance, software updates, and troubleshooting, reducing the need for in-house IT resources.
- Scalable: It’s easy to scale up by adding more users or features through the service provider.
Advantages:
- Lower Upfront Costs: No need to purchase or maintain on-site hardware, which reduces initial investment
- Scalability: Businesses can easily add or remove phone lines or features as needed, making it highly flexible and responsive to businesses’ needs.
- Remote Access: The system administrator can access the cloud PBX from anywhere with an internet connection, making it ideal for remote or distributed teams.
- Automatic Updates: The provider takes care of software updates and security patches, ensuring that the system is always up to date.
Disadvantages:
- Ongoing Subscription Costs: Businesses typically pay a recurring fee for the service, which can add up over time.
- Less Control: Since the PBX is managed by the provider, businesses have less control over system configurations and reliance on the provider for support.
- Dependent on Internet: A stable, high-speed internet connection is essential. Any disruptions in internet service can affect phone system performance.
Best For:
- Small to medium-sized businesses that want a cost-effective, scalable solution with minimal maintenance. Or large enterprises who prefer to outsource the system management and allow their internal IT team to focus on other tasks.
- Businesses with remote or distributed workforces that require access to phone systems from multiple locations.
Hybrid
PBX
A hybrid PBX system combines elements of both on-premise PBX and cloud PBX. It allows businesses to maintain some infrastructure on-site while leveraging the cloud for additional features or flexibility. For example, the core PBX system may be on-premise, but external communication may occur over the internet (VoIP), or some features (like call routing or voicemail) may be hosted in the cloud.
Key Features:
- Mix of On-Site and Cloud Features: Core infrastructure may be on-premise, but some features (like external lines or remote access) are cloud-based.
- Flexibility in Deployment: Offers businesses the ability to maintain control over their PBX system while benefiting from the flexibility and cost savings of the cloud for certain aspects.
- Gradual Migration: Allows businesses to gradually migrate from an on-premise system to a fully cloud-based system over time if needed.
Advantages:
- Best of Both Worlds: Businesses can enjoy the control and customization of an on-premise system while leveraging cloud services for scalability, remote access, or backup.
- Cost-Effective: Allows businesses to minimize on-site hardware while still having the flexibility to integrate cloud features, which can reduce costs in some areas.
- Increased Redundancy: Cloud features can serve as backups, ensuring continuity in case the on-premise system experiences downtime.
Disadvantages:
- More Complex Setup: Combining on-premise and cloud components can require more sophisticated setup and configuration.
- Potential Higher Costs: Maintaining both on-site hardware and cloud services could be more expensive than choosing one approach.
- Requires IT Expertise: Managing a hybrid system may require IT expertise to integrate the two systems smoothly.
Best For:
- Businesses that want the control of an on-premise system but also need the flexibility and scalability of a cloud solution.
- Companies that are transitioning from a traditional PBX system to a cloud-based model and want to do so gradually.
What are the benefits of a PBX system?
Whether you opt for an on-premises, hosted or hybrid PBX each type has to offer many benefits to businesses over traditional phone systems. Below is a short list of the main PBX benefits:
- Cost Savings: Reduces costs by sharing external lines and offering free internal calls.
- Professional Call Management: Features like auto-attendant, call routing, and voicemail enhance call handling.
- Scalability: Easily add extensions or lines as your business grows.
- Internal Communication: Simplifies internal calls via extensions without using external lines.
- Call Routing: Automatically directs calls to the right department or person.
- Advanced Features: Supports features like voicemail, call forwarding, and conferencing.
- Centralized Control: Allows easy management of the entire communication system.
- Improved Customer Service: Call queuing and IVR systems ensure efficient call handling.
- Remote Work Support: Enables employees to access the system remotely or on the go.
- Integration: Can integrate with CRM and other business tools for enhanced productivity.
What to look for in a PBX system

When choosing a PBX system for your business, it’s important to consider several factors to ensure the system meets your current and future communication needs. Here are key aspects to look for:
- Scalability
As your business grows, your PBX system should be able to scale easily. Whether you’re adding new users, departments, or locations, the system should allow seamless expansion without major upgrades or overhauls. Cloud PBX systems typically offer the greatest flexibility for growth, as they allow easy addition of lines and features through a subscription model.
- Features
Modern PBX systems offer a wide range of features to improve communication efficiency. Look for features like auto-attendant, voicemail-to-email, call forwarding, call queuing, video calling, mobile apps, call queues and conference calling. Consider the specific needs of your business—whether you require advanced features like call recording, social media, or CRM integration to streamline operations.
- Cost
Cost is a significant factor in choosing a PBX system. On-premise PBX requires a larger upfront investment for hardware, installation, and ongoing maintenance. In contrast, cloud PBX systems typically have lower initial costs but come with monthly subscription fees. Consider both short-term and long-term costs, including the total cost of ownership (TCO) and whether you have the internal resources to manage the system.
- Ease of Use
A PBX system should be easy to use and manage, both for your employees and your IT team. Look for systems with intuitive interfaces, simple configuration tools, and the ability to make changes (such as adding extensions or rerouting calls) without needing extensive technical knowledge.
- Reliability and Uptime
Your PBX system must be reliable, with minimal downtime, especially if your business depends on constant communication. Check if the provider offers redundancy and failover solutions to ensure uptime. Cloud PBX systems often come with uptime guarantees and disaster recovery options, providing peace of mind that your phone system won’t go down.
- Mobility and Remote Access
If you have a mobile workforce or remote employees, ensure that the PBX system supports remote access. Many VoIP-based and cloud PBX systems allow users to connect via mobile apps or softphones, enabling them to make and receive calls from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Integration with Other Tools
Consider whether the PBX system can integrate with your existing business tools like CRM software, email platforms, or customer support systems. Integration can enhance productivity by enabling features like screen pop-ups for incoming calls or logging calls directly into customer records.
- Security
Security is critical for protecting business communications from fraud, hacking, and unauthorized access. Look for PBX systems with robust security features like encryption, user authentication, and call monitoring to ensure your communication system is safe.
By considering these factors, you can choose a PBX system that fits your business’s needs, providing efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
Adapt a PBX to Your Company — Not the Other Way Around
When selecting a PBX system, it’s crucial to adapt the solution to your company’s unique needs rather than forcing your business to fit into the limitations of the system. Here’s why and how you can achieve that:
- Understand Your Business Needs
Every company has different communication requirements. A small business may prioritize cost-effective internal communication, while a larger organization may need sophisticated features like call routing, queuing, and CRM integration. Start by assessing how your employees communicate, the volume of calls you handle, and whether your business operates in multiple locations or involves remote workers. Your PBX should meet these specific demands without requiring you to change your workflow or add unnecessary complexity.
- Customization and Flexibility
A modern PBX system should offer customization options that allow you to tailor features to your business processes. For example, if your customer support team needs advanced call routing to ensure every inquiry reaches the right agent, the system should provide flexible routing options. Whether it’s custom greetings, time-based call forwarding, or IVR menus, the PBX should mold itself to how you do business, not the other way around.
- Scalability to Support Growth
Your PBX should scale with your company as it grows. This includes adding more users, extensions, or even integrating new communication channels, such as video conferencing or team messaging. Avoid rigid systems that limit your ability to expand or force expensive upgrades. A scalable PBX ensures your business can grow without disrupting its existing communication structure.
- Integrations with Existing Tools
A PBX system that can integrate with your current business tools (such as CRM, helpdesk software, or email platforms) will help streamline operations and boost productivity. You shouldn’t have to overhaul your entire workflow to accommodate your PBX. Instead, choose a system that enhances your existing processes by connecting with the tools you already use.
- Mobility and Remote Work
As businesses evolve, remote work and mobility are increasingly important. Your PBX should support remote employees by allowing them to access the system from anywhere. Look for systems that provide mobile apps or softphone options so employees can remain connected without being physically tied to an office desk.
- Ease of Use and Management
The PBX system you choose should be easy to manage and use. You shouldn’t need a dedicated IT department just to manage the phone system. Features like a user-friendly interface and the ability to make quick changes, like adding extensions or updating call routing, ensure that the PBX works for your business, not against it.
In conclusion, a PBX should adapt to the unique structure, needs, and goals of your company, offering the flexibility, customization, and scalability to fit seamlessly into your existing workflows. By choosing a system that conforms to your business, you ensure smoother communication, reduced disruptions, and long-term efficiency.
Why choose RingQ as your business phone system?

Choosing RingQ as your business phone system comes with a range of benefits tailored to your business needs that achieve enhanced communication, streamlined operations, and improved customer engagement. Here are some compelling reasons to consider RingQ:
- 1. User-Friendly Interface
RingQ offers an intuitive, easy-to-navigate interface that simplifies call management for all users. Whether your team is tech-savvy or not, they can quickly adapt to the system without extensive training.
- 2. Advanced Features
The platform provides a comprehensive suite of features, including call forwarding, voicemail, call recording, conference calling, video calling, mobile apps, wallboard, call queues, reports, IVR/auto-attendant and more. These features enhance communication efficiency and improve customer service.
- 3. Scalability
RingQ is designed to grow with your business. Whether you’re a small startup or a large corporation, adding new users and features is straightforward, making it an ideal solution for businesses of all sizes.
- 4. Cost-Effectiveness
With RingQ, you can significantly reduce communication costs. The system leverages VoIP technology, enabling lower rates for long-distance and international calls, and minimizes the need for expensive hardware.
- 5. Cloud-Based Flexibility
As a cloud-based solution, RingQ allows your team to access the system from anywhere with an internet connection. This is especially beneficial for remote workforces and teams that need to stay connected while on the go. It also means that you won’t need to invest in hardware and dedicated personnel to manage the system in-house.
- 6. Integration Capabilities
RingQ integrates seamlessly with popular CRM and productivity tools, helping you streamline operations and enhance workflows. This integration allows for improved customer management and tracking of communications.
- 7. Reliable Customer Support
RingQ provides robust customer support 24/7 to assist with any issues that may arise. Our knowledgeable team is available to help you troubleshoot and optimize your phone system, ensuring minimal downtime.
- 8. Enhanced Security
Security is a top priority for RingQ. The platform incorporates advanced security measures to protect your communications and data from potential threats, giving you peace of mind.
- 9. Customizable Options
RingQ offers customizable features that can be tailored to fit your specific business needs. From personalized greetings to customized call routing, and even a customizable softphone you can create a system that reflects your brand.
- 10. Performance Analytics
RingQ provides insights and analytics on call performance, allowing you to track metrics such as call volume, duration, and customer interactions. This data can help you make informed decisions to improve service and efficiency.
Conclusion
Choosing RingQ as your business PBX phone system means opting for a flexible, cost-effective solution that prioritizes user experience and customer service. With its advanced features, scalability, and strong support, RingQ is an excellent choice for any organization looking to enhance its communication strategy and foster growth.
Start Today!Get your Free RingQ Trial
PBX Phone System FAQs
A PBX extension is a unique number assigned to a specific phone line or user within a Private Branch Exchange (PBX) system. It allows users to connect with each other internally without needing to dial a full phone number. Extensions streamline communication by simplifying dialing; for example, instead of dialing a full number, users can call an extension like 101 or 205. Extensions also enable features like call forwarding, voicemail, and internal call routing, enhancing overall communication efficiency within a business or organization. They are essential for managing multiple users within the same PBX system.
PBX (Private Branch Exchange) and PABX (Private Automatic Branch Exchange) both refer to telecommunication systems used within organizations. The primary difference lies in their automation level. A PBX can be manual or semi-automatic, requiring operators to manage calls. In contrast, a PABX is fully automatic, using computerized systems to handle call routing and management without human intervention. Both systems allow organizations to manage internal and external phone lines, but PABX systems typically offer more advanced features like call forwarding, voicemail, and automated attendants. Today, PABX has largely become synonymous with modern PBX systems, particularly in VoIP environments.
IP PBX (Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange) is a telephony system that uses Internet Protocol to manage and route voice calls over a network. Unlike traditional PBX systems, which rely on analog or digital phone lines, IP PBX allows voice communications to be transmitted as data packets over the internet or a local area network (LAN). This system offers features like call forwarding, voicemail, and conferencing while reducing costs for long-distance calls. Additionally, it supports remote access, enabling employees to communicate from anywhere. Overall, IP PBX provides a flexible, scalable, and efficient solution for modern business communication.
PBX stands for Private Branch Exchange, a telephone system used within an organization to manage internal and external communications. It connects multiple phone lines and allows users to make calls to each other without using external lines. PBX systems can be traditional (on-premise) or modern (cloud-based), offering features such as call forwarding, voicemail, and automated attendants. By routing calls efficiently, PBX systems enhance communication and reduce costs, especially for businesses with many employees. They play a crucial role in managing telecommunications and improving overall organizational productivity by streamlining voice communication.
PBX (Private Branch Exchange) itself is not a landline; rather, it is a telephone system used to manage and route calls within an organization. However, traditional PBX systems often connect to landlines through analog or digital telephone lines for external communications. In contrast, modern PBX solutions, particularly IP PBX, utilize Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) technology to handle calls over the internet, which may not require traditional landlines. While a PBX can work with landlines, it is versatile enough to function through various communication methods, including VoIP, providing flexibility in how calls are managed and routed.
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) and PBX (Private Branch Exchange) serve different roles in telecommunications. VoIP is a technology that enables voice calls to be transmitted over the internet as data packets, allowing for more cost-effective and flexible communication. In contrast, PBX is a telephone system used within organizations to manage internal and external calls. A PBX can be traditional (on-premise) or IP-based. When combined, VoIP technology can be integrated into a PBX system, resulting in an IP PBX that utilizes VoIP for call routing, offering advanced features and reducing costs compared to traditional PBX systems reliant on analog phone lines.






